Scientific Methods, Protocols and Extra Details of the Barcoding the Harbor Project
Sample collection
Samples are collected monthly by scientists from IMET and the National Aquarium. Samples are scraped from biodisks and stored at -80C. Each is labeled with the date, year, site number, and sample number. Metadata such as water temperature, salinity, etc. are also collected.
DNA extraction
Once brought to the BUGSS lab, DNA is extracted from each sample using the Qiagen DNeasy PowerSoil kit. DNA is measured by NanoDrop and normalized to 10-20 ng/ul.
At this point, each tube of DNA is labeled with a QR code which references an Excel database containing the sample date, year, site number, and sample number. Information about amplification of each sample (such as the primers used for amplification) is added to the database as it is generated (see below).
Amplification of 18S rDNA
The DNA is then amplified to generate a library. Because we are looking to identify eukaryotic organisms, we amplify the 18S ribosomal DNA, although previous experiments at IMET have also amplified the COX-1 (COI) gene. We may in the future study the bacteria present in these samples by amplifying the 16S ribosomal DNA gene.
Our protocols for 18S amplification are based on the protocols of the Earth Microbiome Project and amplify the V9 region using primer 1391forward and 1510reverse as used in the Earth Microbiome Project protocol.
Primer design strategy
Primer design for the library preparation is an important step. We use dual indexed primers, where both the forward and reverse primers contain their own index; this allows us a greater number of primer combinations to uniquely identify each sequence. Our primer design strategy is based on the work of Kozich et al. and is depicted in their figure below. The biggest difference is that our primers anneal to 18S sequences rather than 16S.

Our primers for this project are therefore:
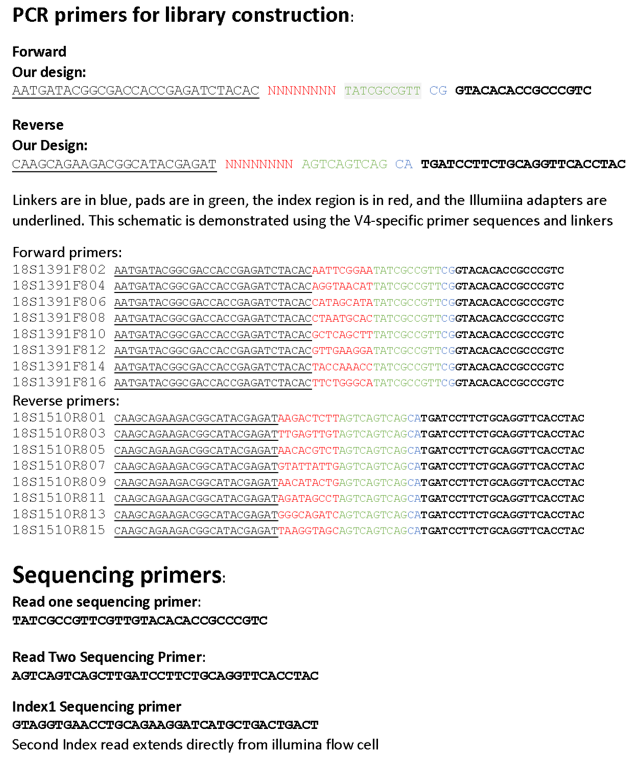
Barcoded primers are ordered in 96-well plates at the 100-nmol scale from IDT or Eurofins Genomics. We do not further purify the oligos, we just use standard desalting. We resuspend our oligos using sterile distilled water to a stock concentration of 100 uM. Dilutions of 10 uM are our working stocks and are used to set up PCR reactions.
18S Amplification Protocol
| Water | 10.5 ul |
| 2X NEB Phusion HotStart 2X Master Mix | 12.5 ul |
| 10 uM forward primer | 0.5 ul |
| 10 uM reverse primer | 0.5 ul |
| Template (10-20 ng/ul) | 1 ul |
| Total volume | 25 ul |
PCR conditions:
| 1 cycle | 94°C | 3 min |
| 35 cycles | 94°C | 45 sec |
| 57°C | 60 sec | |
| 72°C | 90 sec | |
| 1 cycle | 72°C | 10 min |
PCR products are checked by gel electrophoresis on a 1.2% agarose gel using a 100-bp or 2-log DNA ladder. Often, we find that samples will not amplify on the first round but will amplify when subsequently tried again.
Purification of PCR products
To purify our PCR products, we use a SequalPrep Normalization Plate. We add the PCR products directly to the normalization plate, which binds only a defined amount of the DNA. Once eluted from the normalization plate, the PCR products are pooled and purified with a Qiagen PCR purification kit column. When the library is eluted from the Qiagen column, the concentration is checked by NanoDrop; it can also be checked by using a Quantus Fluorometer.
MiSeq Next-Generation Sequencing
Once we have purified DNA, we send it to the Indiana University Center for Genomics and Bioinformatics. (While we haven’t done it for this project, at IU, they can run PicoGreen DNA quantification to check DNA the concentration more accurately than with the NanoDrop. At IU, they perform MiSeq v2 Nano (500 cycle) sequencing, which generates >1 million sequencing reads.